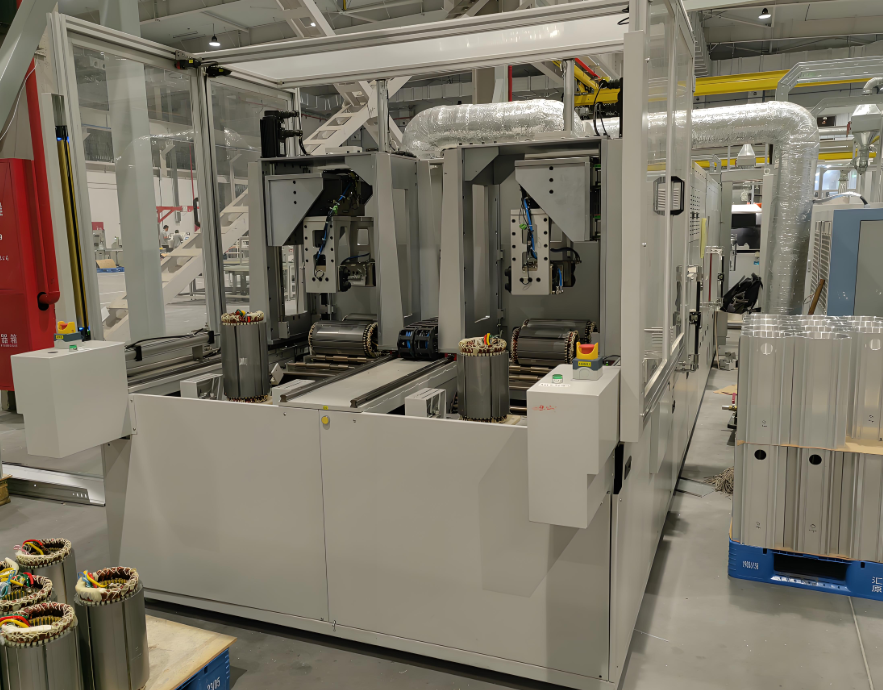
With the acceleration of Industry 4.0, ball screw linear modules are playing a key role in high-end fields such as electronic manufacturing, medical equipment, and new energy batteries due to their unique mechanical properties. According to industry data, the market size of China's linear module has exceeded 8 billion yuan in 2024, with ball screw type accounting for over 65%, becoming the preferred solution for linear motion of automation equipment.
Analysis of Technical Advantages
Nano level repetitive positioning accuracy
Through the precise coordination of ball and screw, the transmission efficiency can reach over 90%, and the repeated positioning error can be controlled within ± 0.01mm, meeting the strict requirements of semiconductor lithography machines, chip mounting and other scenarios. After a certain OLED panel company adopted this module, the yield rate increased by 12%.
Dynamic response capability
Compared to traditional belt transmission, the acceleration can reach 2G or more, and with the cooperation of servo motors, it can achieve a start stop action of 200mm stroke within 0.1 seconds. The application case of a new energy vehicle battery welding line shows a 30% increase in production efficiency.
Long life maintenance free design
The enclosed track structure can effectively prevent dust and has a lubrication cycle of up to 5000 hours. A medical automation enterprise's actual test shows that the accuracy degradation is less than 5% after continuous operation for 30000 hours.
Typical application scenarios
3C industry: assembly of mobile phone camera modules, screen inspection
Photovoltaic industry: positioning of silicon wafer laser cutting
Logistics and warehousing: high-speed sorting robotic arm
Laboratory automation: PCR detection sample transfer
Future Development Trends
As the cost of linear motors decreases, ball screw modules are developing towards "hybrid drive". Industry experts predict that intelligent modules with integrated force control sensors will occupy 30% of the market share by 2026, further expanding the application boundaries of human-machine collaboration scenarios.